The Evolution of Manufacturing ERP Processes
Welcome, dear readers, to a fascinating journey through the evolution of manufacturing ERP processes. In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for streamlining operations, improving efficiency, and maximizing profitability. Join us as we explore the history of manufacturing ERP processes, from their humble beginnings to the cutting-edge technologies shaping the industry today.
Implementation of ERP system in the manufacturing industry
Implementing an ERP system in the manufacturing industry involves a detailed process that requires careful planning and execution. The first step in implementing an ERP system is to identify the needs and requirements of the organization. This involves assessing the current processes, systems, and workflows in place to determine the areas that need improvement or automation.
Once the needs are determined, the next step is to choose the right ERP software that aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives. This includes evaluating different vendors, conducting demos, and selecting the one that best fits the requirements of the manufacturing industry.
After selecting the ERP software, the implementation process begins with creating a project team that will oversee the deployment of the new system. This team typically consists of key stakeholders from various departments within the organization, including IT, finance, production, and supply chain.
The project team is responsible for defining the project scope, setting objectives and goals, creating a timeline, and allocating resources for the implementation process. It’s crucial for the team to communicate effectively and collaborate to ensure a smooth and successful implementation.
One of the key steps in implementing an ERP system is data migration. This involves transferring existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. Data cleansing and validation are essential to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data, which is critical for the system to function effectively.
Training is also a vital component of the implementation process. End-users need to be trained on how to use the new ERP system to maximize its benefits. Training sessions should be tailored to different departments and roles within the organization to ensure that employees are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to operate the system efficiently.
Testing is another crucial phase of the implementation process. The ERP system needs to undergo rigorous testing to identify and address any issues or bugs before it goes live. This includes testing the system’s functionality, integrations, and performance to ensure that it meets the requirements and expectations of the manufacturing industry.
Once the system has been tested and validated, the final step is to go live with the ERP system. This involves transitioning from the old systems to the new ERP system, which may require downtime and disruptions in the manufacturing processes. It’s essential to have a contingency plan in place to minimize any potential risks and ensure a smooth transition.
In conclusion, the implementation of an ERP system in the manufacturing industry is a complex and challenging process that requires careful planning, collaboration, and execution. By following these steps and best practices, organizations can successfully implement an ERP system that will streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth in the manufacturing sector.
Streamlining production processes with ERP
Manufacturing ERP systems are designed to streamline production processes by integrating all aspects of manufacturing operations into one centralized platform. This allows for real-time visibility into production schedules, inventory levels, and order statuses, making it easier for manufacturers to make informed decisions and improve efficiency.
One way ERP systems streamline production processes is by automating manual tasks such as data entry and inventory tracking. By eliminating the need for manual data entry, manufacturers can reduce the risk of human error and save time that can be better spent on more value-added activities. Automated inventory tracking also ensures that manufacturers have accurate and up-to-date information on inventory levels, preventing stockouts and reducing the risk of overstocking.
In addition to automation, ERP systems also standardize and centralize production processes, making it easier for manufacturers to maintain consistency and quality across their operations. By having a single source of truth for production data, manufacturers can ensure that all departments are working with the same information and following the same procedures. This helps to reduce errors and inconsistencies and improve overall production efficiency.
Another way ERP systems streamline production processes is by providing real-time visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production output, quality metrics, and equipment utilization. By having access to this information in real-time, manufacturers can quickly identify areas of inefficiency and take corrective action to improve productivity. This is especially important in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, where even small improvements in efficiency can have a significant impact on the bottom line.
ERP systems also facilitate better communication and collaboration among different departments within a manufacturing organization. By centralizing all production data and processes in one system, ERP systems make it easier for departments such as production, inventory management, and quality control to work together seamlessly. This improved communication and collaboration help to reduce bottlenecks and streamline production processes, leading to faster lead times and better customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, manufacturing ERP systems play a crucial role in streamlining production processes by automating manual tasks, standardizing production processes, providing real-time visibility into KPIs, and facilitating better communication and collaboration among different departments. By leveraging the power of ERP systems, manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment.
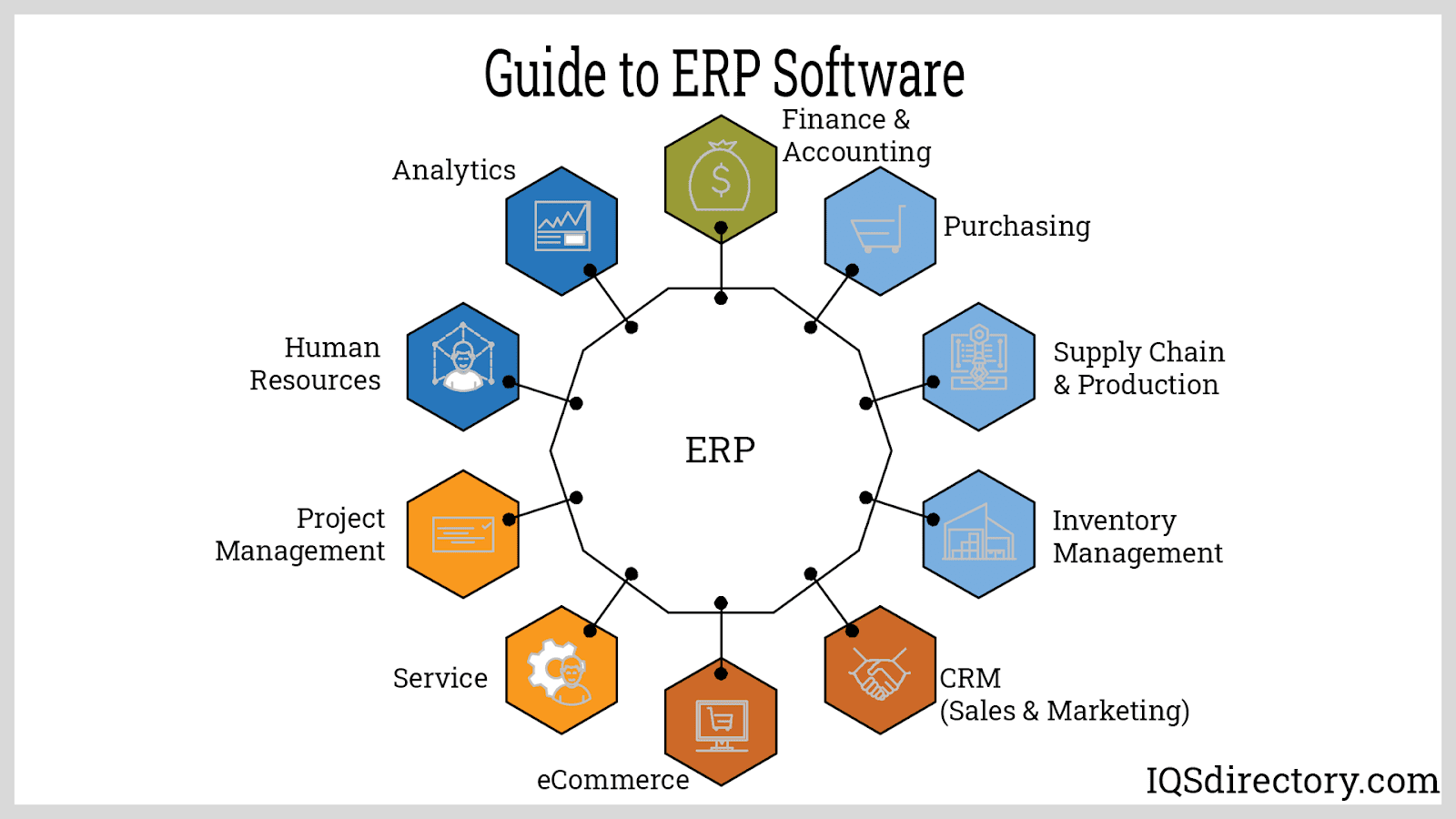
Key features of ERP for manufacturing companies
Manufacturing companies rely heavily on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to streamline their processes, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. There are several key features of ERP systems that are specifically tailored to meet the unique needs of manufacturing companies.
One of the most essential features of ERP for manufacturing companies is inventory management. Manufacturing operations involve complex supply chains and large inventories of raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished products. An ERP system helps manufacturers keep track of their inventory levels in real-time, prevent stockouts, and optimize their production schedules based on inventory availability.
Another important feature of ERP for manufacturing companies is production planning and scheduling. Manufacturing processes must be carefully planned and coordinated to ensure optimal resource utilization and timely delivery of products. An ERP system integrates production planning and scheduling with other functions such as inventory management, procurement, and quality control, enabling manufacturers to create accurate production schedules, allocate resources efficiently, and minimize production lead times.
Furthermore, quality control is a critical feature of ERP for manufacturing companies. Quality control processes are essential to ensure that products meet customer specifications and regulatory requirements. An ERP system can help manufacturers implement quality control procedures, track and analyze product quality data, and identify and address quality issues in real-time. By integrating quality control with other functions such as production, inventory, and procurement, an ERP system enables manufacturers to improve product quality, reduce defects, and enhance customer satisfaction.
In addition, supply chain management is another important feature of ERP for manufacturing companies. In today’s globalized business environment, manufacturers must manage complex supply chains involving multiple suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers. An ERP system can help manufacturers optimize their supply chains, track and manage orders, shipments, and deliveries, and collaborate with supply chain partners to improve efficiency and reduce costs. By integrating supply chain management with other functions such as production planning, inventory management, and quality control, an ERP system enables manufacturers to achieve greater visibility and control over their supply chains.
Overall, ERP systems offer a comprehensive suite of features that are specifically designed to meet the unique needs of manufacturing companies. From inventory management to production planning, quality control, and supply chain management, ERP systems provide manufacturers with the tools they need to streamline their processes, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions. By leveraging the key features of ERP, manufacturing companies can enhance their competitiveness, increase customer satisfaction, and drive growth and profitability in today’s dynamic business environment.
Benefits of using ERP in the manufacturing sector
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become an essential tool for modern manufacturing businesses. These systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization, including manufacturing, finance, sales, and service. The benefits of using ERP in the manufacturing sector are numerous and can greatly improve productivity, efficiency, and decision-making.
1. Increased Efficiency: One of the primary advantages of implementing an ERP system in the manufacturing sector is the increase in efficiency. By centralizing data and processes, ERP eliminates the need for manual data entry and streamlines business operations. This results in reduced lead times, improved inventory management, and better resource allocation.
2. Enhanced Visibility: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into all areas of the manufacturing process. This allows managers to track production schedules, monitor inventory levels, and analyze performance metrics. With this level of visibility, decision-makers can make informed choices that optimize production and minimize waste.
3. Integrated Communication: ERP systems facilitate seamless communication between different departments within a manufacturing organization. By consolidating information in a centralized database, employees can access and share data easily, leading to better collaboration and coordination. This integrated communication streamlines workflows and reduces errors caused by miscommunication.
4. Improved Decision-Making: One of the key benefits of using ERP in the manufacturing sector is the ability to make data-driven decisions. ERP systems generate accurate and up-to-date reports and analytics, providing managers with the insights they need to identify trends, spot inefficiencies, and devise strategies for improvement. With access to this comprehensive data, decision-makers can respond quickly to changing market conditions and make informed choices that drive business growth.
5. Cost Savings: Implementing an ERP system in the manufacturing sector can lead to significant cost savings over time. By streamlining processes, reducing manual work, and improving resource utilization, ERP helps organizations operate more efficiently and effectively. This results in lower operational costs, reduced waste, and increased profitability.
6. Regulatory Compliance: Manufacturing businesses are subject to a multitude of regulations and compliance requirements. ERP systems help companies adhere to these regulations by providing tools for tracking and documenting compliance activities. This ensures that manufacturing processes meet legal standards and reduce the risk of penalties or fines.
Overall, the benefits of using ERP in the manufacturing sector are vast. From increased efficiency and enhanced communication to improved decision-making and cost savings, ERP systems have the potential to transform manufacturing operations and drive business success. By leveraging the power of ERP technology, manufacturing businesses can stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
Challenges in integrating ERP into manufacturing operations
Implementing an ERP system in a manufacturing environment can be a complex and challenging process. There are several obstacles that organizations face when integrating ERP into their manufacturing operations.
1. Resistance to Change: One of the main challenges in implementing ERP in manufacturing is overcoming resistance to change among employees. Many workers may be comfortable with the existing system and processes, and may be hesitant to adapt to a new way of working. It is important for management to clearly communicate the benefits of the ERP system and provide training and support to help employees transition smoothly.
2. Data Migration Issues: Another hurdle in integrating ERP into manufacturing operations is the migration of data from existing systems to the new ERP platform. This process can be time-consuming and complex, as it involves transferring large volumes of data while ensuring accuracy and consistency. It is crucial for organizations to have a clear data migration plan in place to minimize disruptions during the transition.
3. Customization and Configuration: ERP systems are often highly customizable to fit the specific needs of different industries and organizations. However, this customization process can be challenging and resource-intensive, requiring expertise in both ERP software and manufacturing processes. It is essential for companies to carefully map out their requirements and work closely with ERP vendors to ensure that the system is configured correctly.
4. Integration with Existing Systems: Many manufacturing companies have a complex IT landscape with multiple systems and applications in place. Integrating the ERP system with existing systems such as CRM, inventory management, and production planning can be a major challenge. It is important for organizations to conduct a thorough integration analysis and plan ahead to ensure a seamless connection between the ERP system and other systems.
5. Change Management: One of the key challenges in integrating ERP into manufacturing operations is managing the organizational change that comes with implementing a new system. Change management involves addressing the concerns and resistance of employees, providing training and support, and establishing clear communication channels to keep everyone informed throughout the process. It is crucial for companies to have a dedicated change management team in place to facilitate a smooth transition and ensure the successful adoption of the new ERP system.
In conclusion, integrating ERP into manufacturing operations is a complex process that requires careful planning, communication, and management. By addressing these challenges head-on and taking proactive steps to overcome them, organizations can successfully implement an ERP system that improves efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making in their manufacturing operations.
Originally posted 2024-08-28 11:54:19.